
Image by 💖MORE ON 👉 https://melovess.com 💖 from Pixabay
Data Operations (DataOps), Data Science, and Data Engineering are three closely related fields in data management and analytics. While Data Science involves the development of statistical and machine learning models to extract insights and make predictions from data, DataOps focus on the processes and tools used to manage, integrate, and deploy these models in production environments. Data Engineering is the practice of designing, building, maintaining, and managing data pipelines and systems that enable organizations to store, process, and analyze large and complex datasets.
What we’ll cover
- What is DataOps?
- DataOps and Data Engineering
- Data Ops and Data Science
What is DataOps?
DataOps is a term used to describe developing and managing data-driven applications. It encompasses the entire data lifecycle, from its collection and storage to its processing and analysis.
DataOps is a relatively new field, and as such, there is no one agreed-upon definition of it. However, most experts agree that DataOps involves the following key components, as shown in the following figure:
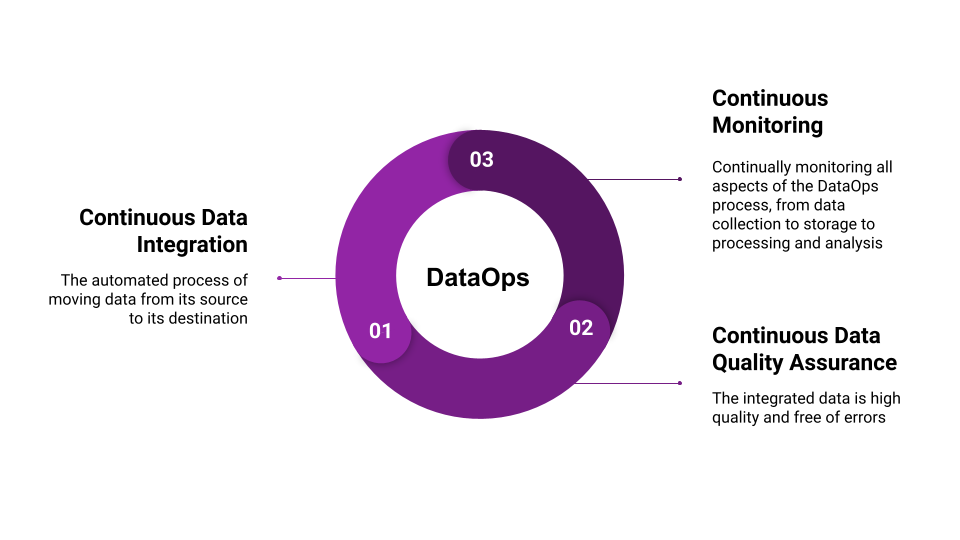
The DataOps main components
- Continuous data integration: This refers to the automated process of moving data from its source to its destination. This can be done using various tools, including ETL (extract, transform, load) tools and data pipelines.
- Continuous data quality assurance: This component ensures that the integrated data is high quality and free of errors. Data quality assurance can be achieved through manual and automated methods.
- Continuous monitoring: This refers to continually monitoring all aspects of the DataOps process, from data collection to storage to processing and analysis. Monitoring helps identify issues early on so they can be addressed in a timely manner.
DataOps engineers help people produce meaningful results faster, in a more pleasant, less scary way. DataOps is not only about infrastructure; it’s also about helping people write better SQL queries and learn how to use the infrastructure.
How is DataOps related to infrastructure?
DataOps is related to infrastructure in several ways. First, DataOps relies on automation to manage and provision infrastructure resources. This allows for faster deployments and updates and reduces the need for manual intervention.
Additionally, DataOps uses monitoring and logging tools to track the performance of infrastructure resources. This helps identify issues early and prevent them from becoming critical problems.
Finally, DataOps includes disaster recovery plans that ensure the continuity of operations in the event of an infrastructure failure.
Suitable skills for DataOps
DataOps is a data management approach that emphasizes collaboration, automation, and monitoring to help organizations improve their data pipelines’ speed, quality, and security. To succeed in a DataOps role, you must have strong technical skills and work well with others.
You will serve as a middleman between the platform, security, SRE, and users, meaning data analysts, engineers, and scientists. And as a DataOps role, you work across different teams and business units. You are also observing some Slack channels.
DataOps and Data Engineering
There is a lot of overlap between DataOps and Data Engineering. Both disciplines deal with data management, including data acquisition, storage, transformation, and analysis. Both also strongly emphasize automation and using tools and technologies to streamline processes and improve efficiency.
However, there are some critical differences between the two disciplines. DataOps primarily focuses on operations, ensuring that data pipelines run smoothly and efficiently. On the other hand, Data Engineering focuses on designing and implementing those data pipelines.
DataOps practitioners need to have a strong understanding of both the technical aspects of data management and the business goals that need to be achieved. Data Engineers need to be experts in designing and building scalable data architectures that can support the needs of a rapidly growing business.
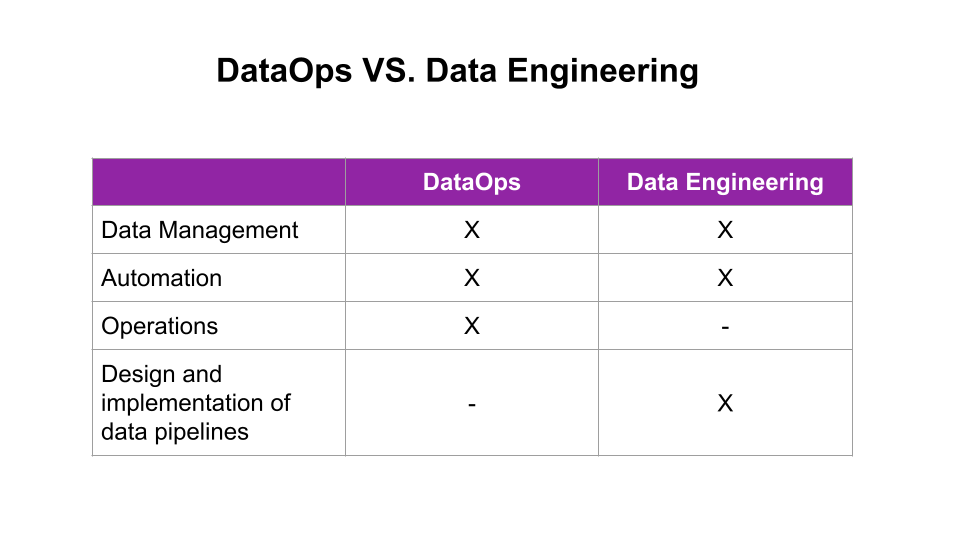
DataOps VS. Data Engineering
DataOps and Data Science
In the past, Data Science and DataOps were often treated as separate disciplines, with data scientists developing models and data engineers handling the deployment and maintenance of those models. However, as the demand for data-driven decision-making has increased, the importance of DataOps has grown, and the lines between these two fields have become increasingly blurred.
One reason for this is that the success of a data science project often depends on the quality and availability of data, as well as the speed and reliability of the model deployment process. As a result, data scientists are increasingly being asked to take on DataOps responsibilities, such as data integration, model deployment, and monitoring.
This shift has led to the emergence of a new role known as the “data scientist-engineer,” or “data scientist 2.0,” skilled in both data science and DataOps. These professionals bridge the gap between the development of statistical models and their practical implementation, ensuring that data science projects are delivered on time and with high quality.
Another important factor driving the convergence of Data Science and DataOps is the increasing use of cloud-based platforms and tools. These platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure, provide data scientists with access to a wide range of tools and services for data storage, processing, and analytics as automatic scaling and deployment capabilities.
This has made it easier for data scientists to deploy and maintain models in production environments. It has also led to the developing of new tools and frameworks designed explicitly for DataOps, such as Apache Airflow and Databricks.
In summary, the distinction between Data Science and DataOps is becoming increasingly blurred as data scientists are increasingly being asked to take on DataOps responsibilities, and cloud-based platforms and tools make it easier for data scientists to deploy and maintain models in production environments. The emergence of the data scientist-engineer role, with skills in data science and DataOps, reflects this trend.
Summary
Congratulations! You have just learned what DataOps is and its differences and similarities with Data Engineering and Data Science.
- DataOps involves developing and managing data-driven applications
- DataOps focuses on operations, ensuring that data pipelines run smoothly and efficiently. Data Engineering focuses on designing and implementing those data pipelines.
- Data Science and DataOps are two separate fields. However, data scientists are increasingly being asked to take on DataOps responsibilities.